Worrying about low testosterone has become one of the latest health panics. It doesn’t help that testosterone is, both biologically and culturally, so important to the male ideal. As a result, while it may seem overdramatic, accusing soy of killing testosterone is actually poking at some of men’s deepest insecurities.
It makes a convenient string to pull on, but it’s not entirely on the level. Your diet can certainly impact testosterone. However, the relationship between diet and testosterone levels is more complex than some would have you believe.
Key Takeaways: Foods That Lower Testosterone
- Your overall health, fitness, and daily habits have a more significant impact on testosterone than any single food.
- Foods may either raise or lower testosterone depending on a variety of factors, including any health conditions.
- Some foods that are popularly thought to reduce testosterone, such as flaxseed and soy, won’t affect testosterone levels in healthy people.
- Drinking large amounts of alcohol, particularly on a regular basis, will decrease testosterone levels.
- Higher levels of body fat and a sedentary lifestyle will also lower testosterone, as will a diet heavy in sugar and unhealthy fats.
- Eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly is the best way to support healthy testosterone levels.
- The quickest way to increase testosterone is a resistance workout, followed by protein supplementation.
Testosterone Killing Foods
Foods that have the reputation of reducing the level of male hormones include:
- Alcohol.
- Mint.
- Flaxseed.
- Soy products.
- Sugar.
- Trans fats and processed foods.
- Licorice root.
- Some nuts.
- Coffee.
It’s dramatic to talk about the foods that kill testosterone. However, a simple list of such foods is always going to be, to some degree, misleading. Research shows that the same foods that decrease T-levels in some cases may increase it in others. In truth, your overall health will have a greater effect on free testosterone and serum testosterone levels than any single food.
Looking more deeply into their effects on sperm count, the status of androgen receptors and testosterone levels reveals more complex relationships. As a result, in most cases, more research is required before we can truly claim to understand the relationship between diet and testosterone levels.
Alcohol
Alcohol is a great example of why it’s difficult to say a particular food will absolutely kill testosterone. Depending on a number of factors, alcohol could raise or lower T-levels.
Smaller amounts of alcohol, perhaps a single glass, may briefly increase testosterone production. Heading out for a beer after a workout, though just the one, may help get the most out of exercise. However, you’d probably get a larger, healthier bump by supplementing protein.
On the other hand, chronic drinking or drinking large amounts will decrease testosterone. Moreover, chronic drinking has wider health effects that may also impact testosterone levels [1].
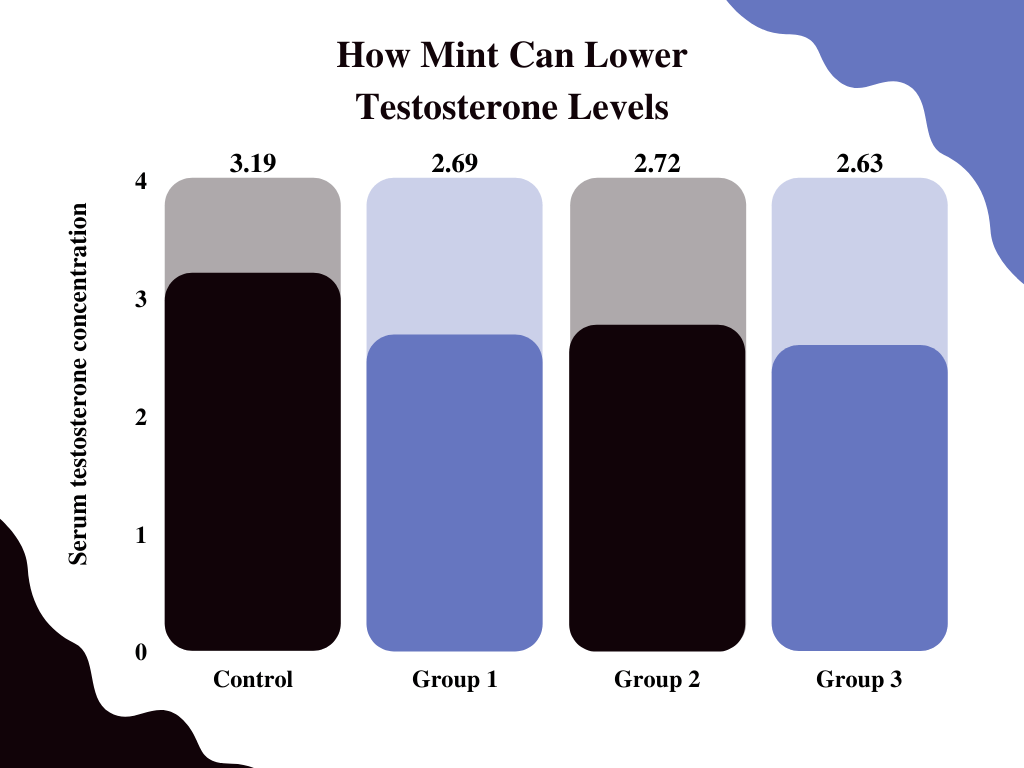
Mint
Research shows on rats shows that high doses of mint have a paradoxical effect. It can increase the levels of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone, both of which are important in testosterone production.
At the same time it’s increasing those testosterone building blocks, mint was also found to lower testosterone levels. The counterintuitive effect suggests that there is a more complex relationship between mint and testosterone levels that is not yet well understood.
However, the drop in testosterone was not considered significant. You can still have minty-fresh breath without worry [2].
Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4224956/
Flaxseed
Flaxseed effects on testosterone can be profound, though the effect on hormone levels is not the same in everyone. It is sometimes claimed that flaxseed contains estrogen and that more estrogen will negatively impact T-levels. However, neither of those claims is wholly correct.
Flaxseed contains plant compounds called enterolignans, which are similar in many ways to estrogen. They will bind with many estrogen receptors, for example.
However, enterolignans aren’t the same as estrogen, so there are some things they can’t do. In particular, estrogen is a key ingredient in making testosterone, a process in which enterolignans can’t substitute.
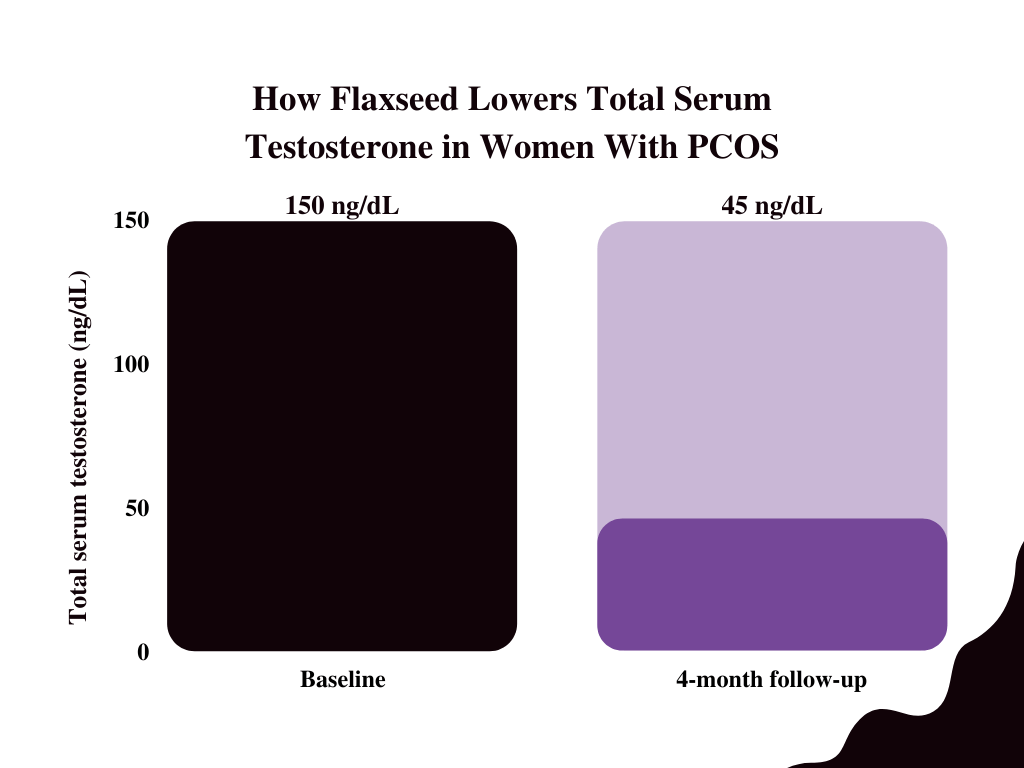
As a result, flaxseed supplementation can be helpful in balancing hormone levels, among other health benefits. For example, it’s been shown to help reduce unhealthy testosterone levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome, leading to a more regular menstrual cycle. It may also lessen the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Flaxseed does not seem to have a significant effect on testosterone levels in otherwise healthy people, however [3].
Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2752973/
Soy
Soy foods are frequently picked out as food that lowers testosterone production. Criticism ranges from soy protein being less effective for building muscle mass, to soy milk actively making you less masculine [4] [5].
There was some early evidence that phytoestrogen isoflavones from soy could lower T-levels based on animal studies. However, follow-up studies in humans have not shown the same effect. In a randomized controlled trial, men eating soy products did not have lower T-levels or sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) levels than those in the control group.
It appears humans don’t metabolize soy in the same way rats do, so any evidence using them as a human model in experiments evaluating soy is suspect [6].
Other studies have shown that eating soy lowers your risk of prostate cancer, while soy protein may help prevent oxidative stress. That in turn can have a number of positive effects, like helping you gain lean body mass, as well as potentially preventing health problems later in life.
Sugar
Small amounts of sugar aren’t a problem, but minimizing sugar intake is increasingly difficult. Most people know that sugar creates hormonal imbalances in the form of diabetes, though it’s not often discussed in terms of hormones.
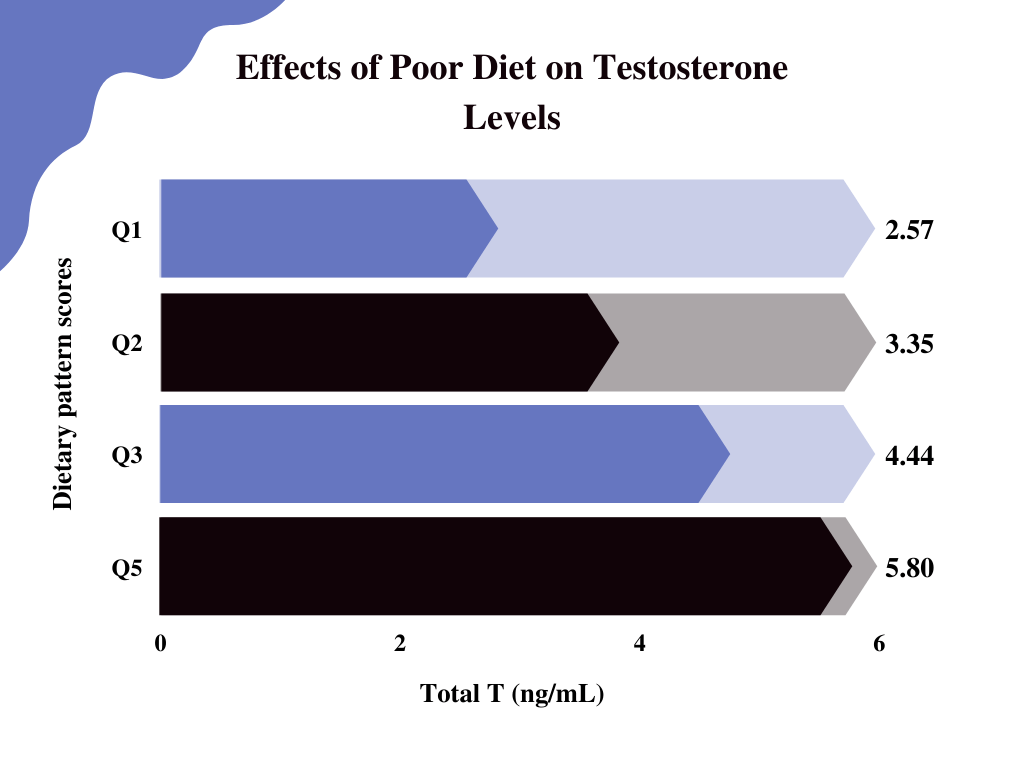
Diabetes can be one aspect of a larger issue called metabolic disorder, in which large amounts of sugar and refined carbohydrates throw your entire body chemistry out of whack.
In addition to weight gain, increased blood pressure, increased risk of heart disease, and higher cholesterol levels, metabolic disorder also can severely, negatively impact T-levels. Low testosterone means you’re more likely to put on weight, which in turn can make metabolic disorder worse. The downward spiral becomes increasingly difficult to escape [7].
Trans Fats and Processed Foods
Most foods that will impact testosterone levels negatively are also foods that are bad for you generally. Topping that list are highly processed foods like fried foods, many frozen foods, foods heavy with refined carbs, and anything with a lot of trans fats.
Food manufacturers process foods for a variety of reasons, including a longer shelf-life. In doing so, many nutrients and most flavor are removed, then replaced with vegetable oils, carbs, and sugar. This is one reason to avoid soy-based foods, as soy is often used in processed foods, though it’s the processing and not the soy that’s a problem.
Similar to sugar, the result can be metabolic disorder, weight gain, loss of muscle mass, and a reduction in free testosterone production [8].
Note that all fat isn’t bad. Some types, like polyunsaturated fatty acids, are required for good health.
Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6266690/
Licorice
Licorice root, particularly the active ingredient glycyrrhetinic acid, can negatively affect testosterone levels. The effect was not significant in men, with no effect on testicular function, or sperm quality. However, the effect was more pronounced in women factors affecting testosterone [9].
Certain Types of Nuts
There is a lot of confusion regarding nuts and their effects on testosterone. Will almonds help or hurt you? How about walnuts? Like with the other foods on this list, there’s no simple rule to follow.
Some compounds in nuts have been shown to reduce testosterone levels in rats, while others increase it. The effects can also vary depending on the amount of the various compounds in the variety of nuts and the health of the person eating them. Looking at some examples might help clarify things:
- Hazelnuts: In older rats, supplementing hazelnuts increased testosterone. Younger rats didn’t see a similar increase, however.
- Walnuts: A compound in walnuts, linoleic acid, increases testosterone in mice. Higher doses may have damaged testicular tissue in rabbits, however.
- Peanuts: One compound found in both peanuts and red wine, resveratrol, was shown to increase a building block of testosterone, luteinizing hormone, in rats.
Mixed results and a lack of human studies means it should probably all be regarded skeptically.
On the other hand, nuts are a great source of healthy fats, like monounsaturated fatty acids, which you need for good health. Concerns over low testosterone levels are probably not a good reason to avoid them [10].
Dairy Products
Milk’s evolutionary purpose is to provide newborns with nutrients and other compounds required to further develop. As a result, the hormone levels in milk and other dairy products, particularly estrogen levels, can be high. Studies suggest that those hormones do have an effect on health, for example, increasing the incidence of acne among teenage boys [11] [12].
The level of estrogen in milk, along with other factors, may also increase your chances of prostate cancer. Additionally, in many cases, it seems the ratio of estrogen to testosterone is important, so raising estrogen levels may have a similar effect to lowering testosterone levels. However, evidence remains thin regarding the direct effects of dairy on testosterone.
Coffee
Coffee doesn’t appear to affect healthy hormone levels. Studies have found that another hormone, SHBG, can be increased to some degree in women after drinking coffee.
SHBG binds with testosterone so it can’t be used in other functions, like building muscle. It may seem natural to assume raising the level of that compound would therefore lower T-levels.
However, the relationship is not so direct. Despite higher levels of sex hormone-binding globulin, everything stayed within healthy levels, and there appeared to be no meaningful effect on T-levels [13].
What Foods Increase Testosterone?
The quality of your general diet and health is going to play a more important role in increasing testosterone levels than any individual food. Trying to come up with a list of foods that increase testosterone is no simpler than discovering which may be a testosterone killer and for a similar reason.
In the same way that an unhealthy diet can decrease testosterone, healthy eating can support healthy T-levels. Don’t bother avoiding soy products. Instead, reduce vegetable oils and trans fats. However, don’t skip out on healthy fatty acids, like polyunsaturated fats. The more nutrients you can get from fruits, vegetables, and a limited amount of lean protein, the healthier your T-levels will be.
Note that a healthy diet will not increase testosterone beyond healthy levels, as that would be just as unhealthy as levels that are too low.
How To Boost Testosterone Naturally
Not to belabor the point, but the best way to positively affect testosterone levels is to improve your overall health. A high-fat diet, low levels of exercise, and weight gain are all associated with low testosterone levels. As a result, plenty of exercises and a diet low in trans fats can increase testosterone. Getting plenty of nutrients like protein and vitamin D through your diet is also important, and getting enough sleep will support healthy T-levels.
When natural methods don’t suffice, testosterone replacement therapy may be necessary. It involves taking synthetic hormones under a doctor’s direction. That sort of treatment is usually only prescribed when illness or disease reduces testosterone. The normal drop due to age doesn’t require replacement therapy.
Exercise To Increase Testosterone
When it comes to exercise, any variety can be helpful. Cardio workouts are better at burning fat, which can help bring hormonal levels back into balance. Any amount of exercise, even a brief walk each day, can be helpful.
However, the single best way to increase testosterone is resistance exercise. Examples include exercises like:
- Push-ups.
- Squats.
- Chin-ups.
- Bicep curls.
- Deadlifts.
- Any sort of weight lifting.
Any exercise that involves resistance to motion is the best for building muscle. Building muscle requires higher amounts of testosterone, so your body will start making more.
Low testosterone in women may not be a problem, as they generally require less. However, they can experience a similar benefit by lowering levels of the stress hormone cortisol. Exercise is also a good method of doing that.
FAQ
Want to ask one of these common questions? We’ve got the answers.
What Are the 5 Foods That Kill Testosterone?
There are many lists of foods that kill testosterone on the internet, each containing a range of foods. Some are the same as those in our list above, though there aren’t five foods that are generally agreed to most negatively impact testosterone levels.
The reality is that your overall health has a greater effect on your testosterone levels than any particular food. Additionally, the effects different foods may have will differ depending on the state of your health. For example, flaxseed will lower testosterone in women with PCOS, but won’t affect the T-levels of people who are generally healthy.
Which Foods Increase Testosterone the Most?
While there isn’t a single food that will inevitably raise testosterone levels in everyone, there are a few foods that can offer a bump to testosterone.
The top of the list is protein, particularly from red meat. Testosterone is an important part of the process which breaks protein down and turns it into muscle. If your body has more protein to process, then it will produce more testosterone to meet the need. Many weightlifters will eat a protein bar or something similar after a workout to take advantage of that fact.
Other foods that may help support healthy testosterone levels include:
- Garlic.
- Ginger.
- Walnuts.
- Vitamin C.
- Turmeric.
Note that if you already have healthy testosterone levels, eating these foods may not increase it further.
Does Masturbation Decrease Testosterone?
Sexual activity of any kind could increase testosterone levels. Testosterone, among its many other roles, is important in the production of sperm. Particularly after an ejaculation, testosterone levels get a bump to make more [14].
Do Bananas Lower Testosterone?
One compound in bananas called bromelain has been noted as potentially increasing testosterone. Studies have shown it to improve testicular function in rats, as well. However, further studies in humans are needed before its effects can be accurately gauged [15].
What Habits Reduce Testosterone?
If you’re wondering how to lower testosterone levels, you’re in luck. You can skip the trip to the gym and stock up on junk food. Testosterone tends to be lower in sedentary people with a higher ratio of body fat.
Additionally, an irregular sleep schedule can also decrease testosterone levels. Staying healthy and eating well will keep T-levels healthy, on the other hand.
Conclusion
It’s tempting to draw straight lines between specific foods and health effects. It would make life a lot easier if we could swear off tomatoes and never have to worry about low testosterone again, or something along those lines.
However, the human body is a stupefyingly complex machine, with thousands of interrelated processes, all struggling to stay in balance. It’s been hundreds of years after the founding of modern, scientific medicine, and we’re only just beginning to understand ourselves.
Or in other words, it’s a good idea to be skeptical of any claims that specific foods lower testosterone.
References:
- Sarkola, Taisto, and C. J. Peter Eriksson. “Testosterone Increases in Men after a Low Dose of Alcohol.” Wiley Online Library, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 30 May 2006, https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1530-0277.2003.tb04405.x.
- Akdogan, Mehmet, et al. “Effects of Peppermint Teas on Plasma Testosterone, Follicle-Stimulating Hormone, and Luteinizing Hormone Levels and Testicular Tissue in Rats.” Urology, Elsevier, 7 Aug. 2004, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0090429504004182.
- Parikh, Mihir, et al. “Dietary Flaxseed as a Strategy for Improving Human Health.” MDPI, Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute, 25 May 2019, https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/11/5/1171/htm.
- Brown, Erin C, et al. “Soy versus Whey Protein Bars: Effects on Exercise Training Impact on Lean Body Mass and Antioxidant Status.” Nutrition Journal, BioMed Central, 8 Dec. 2004, https://nutritionj.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1475-2891-3-22.
- Gambert, Iselin, and Tobias Linné. “From Rice Eaters to Soy Boys: Race, Gender, and Tropes of ‘Plant Food Masculinity’.” SSRN, 31 Dec. 2018, https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3298467.
- Messina, Mark. “Soybean Isoflavone Exposure Does Not Have Feminizing Effects on Men: a Critical Examination of Clinical Evidence.” Fertility and Sterility, Fertility and Sterility, 8 Apr. 2010, https://www.fertstert.org/article/S0015-0282(10)00368-7/fulltext.
- Hu, Tzu-Yu, et al. “Testosterone-Associated Dietary Pattern Predicts Low Testosterone Levels and Hypogonadism.” MDPI, Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute, 16 Nov. 2018, https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/10/11/1786/htm.
- Gates, Margaret A, et al. “Sex Steroid Hormone Levels and Body Composition in Men.” The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, Endocrine Society, June 2013, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3667256/.
- Manuel, M. Leo Bernard, and Dr Gayathri. “Factors Affecting Testosterone Level In Men.” International Journal for Research Trends and Innovation, International Journal for Research Trends and Innovation, 2021, https://ijrti.org/papers/IJRTI2103029.pdf.
- Kataoka, Tomoya, et al. “A Review of Foods and Foods Supplements Increasing Testosterone Levels.” Journal of Men’s Health, Journal of Men’s Health, 20 Nov. 2020, https://oss.jomh.org/jomh/article/20210409-243/pdf/4-14%20JOMH348.pdf.
- Qin, Li-Qiang, et al. “Estrogen: One of the Risk Factors in Milk for Prostate Cancer.” Medical Hypotheses, Churchill Livingstone, 27 Nov. 2003, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0306987703002950.
- Adebamowo, Clement A., et al. “Milk Consumption and Acne in Teenaged Boys.” Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, Mosby, 14 Jan. 2008, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0190962207024024.
- Wedick, Nicole M, et al. “The Effects of Caffeinated and Decaffeinated Coffee on Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin and Endogenous Sex Hormone Levels: A Randomized Controlled Trial.” Nutrition Journal, BioMed Central, 19 Oct. 2012, https://nutritionj.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1475-2891-11-86.
- Turgut, Hasan, and Guner Kemal Ozgur. “Does Masturbation Frequency Effect Sperm.” Andrology, Journal of Urological Surgery, 2020, http://cms.galenos.com.tr/Uploads/Article_40011/JUS-7-200-En.pdf.
- Jebur, Ali B., et al. “Bromelain from Ananas Comosus Stem Attenuates Oxidative Toxicity and Testicular Dysfunction Caused by Aluminum in Rats.” Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, Urban & Fischer, 1 Aug. 2020, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0946672X20301966.